It was a fearsome crime and although newspapers in those days were packed with stories about terrible murders, this incident was so horrific that news of it spread nationwide, becoming the first time most Americans heard of a place called Sonoma county. Even your great -great (-great?) grandmother Augusta in far-away Minnesota read this wire story on the front page of her local paper in 1886:
| CLOVERDALE, Cal., Jan 23–Details reached here to-day of a double murder, the victims of which are a prominent farmer, Jesse C. Wickersham, and wife….Wickersham was found sitting in a chair in the diningroom dead, with blood oozing from a wound in the breast and another in the head. Mrs. Wickersham was found dead on the bed in a bed-room up stairs, her hands and feet bound and a wound in her breast. The valuables on both bodies were intact, which showed robbery was not the object of the crime. All the wounds were inflicted by a shotgun. Strong circumstantial evidence points to a Chinese cook, Ah Kai, employed by the murdered couple. Ah Kai is nowhere to be found…1 |
| – | – | THE WICKERSHAM MURDERS MANHUNT II: HOW (NOT) TO CATCH A FUGITIVE SOURCES (PDF, 31 pages) |
The picture it painted portrayed nightmarish scenes: A woman tied up on her bed, the gruesome view of her husband, the idea that both were innocents slaughtered senselessly by a member of their household. That the supposed mad killer was a Chinese immigrant only confirmed what fear-mongering politicians and the press had been shouting for years.
But aside from the Wickershams indeed being murdered, most of the important facts in the article were wrong. Robbery probably was the motive; no evidence implicated the Chinese cook, who immediately became the prime suspect only because his whereabouts were unknown and other (more likely) culprits weren’t considered.
The Wickersham killings had an immediate impact on Sonoma county and the state, leading to boycotts of Chinese businesses and expulsion of immigrants from towns – and its ripples even reached Congress as more anti-Chinese legislation passed in the following years. But despite its importance. actual details of the Wickersham case never have been closely examined.
What follows is part one, which dives into the conflicting stories about the double murder; parts two and three follow the manhunt for the Chinese cook and part four suggests who were the more likely suspects.
This is a tricky tale to write because every newspaper added, omitted and/or contradicted details found in other papers. Often the differences were minor – but sometimes they were critical to interpreting events. In almost every case I selected a version that came from an interview with someone with first-hand knowledge, but some players were so eager to implicate the Chinese man that they apparently lied or exaggerated, and in one case, possibly tampered with the crime scene. Any non-trivial differences are discussed. If you want the complete scoop, newspaper transcriptions for the whole series will be available for download in a separate text file.
As we begin, keep in mind this is an important moment in our history only because of a perfectly awful set of circumstances. Had the Wickershams been murdered six months earlier or later the tragedy might have been little noticed – but it happened at the peak of local anti-Chinese frenzy. Had the Wickersham ranch not been so hard for authorities to reach, accurate details might have been reported quickly – instead, newspapers fed the public’s hunger for news by printing lies and rumors. And even Mother Nature seemed to conspire to make any possible investigation difficult – there was a Perfect Storm before the crime was discovered which likely obliterated evidence.
 |
|
Location of the Wickersham ranch and vicinity on the map from the 1898 county atlas
|
The winter of 1885-1886 was fairly mild and dry in Sonoma county – except for the third week of January, when the North Bay was slammed with torrential rains and high winds. There was snow on St. Helena and Sonoma Mountains; major roads were impassible, with the well-traveled route through the Sonoma Valley compared to a lake.
It was just before the biggest storm hit on Wednesday the 20th when two Indians showed up at Elliott Jewell’s ranch, far from any town in the rugged northwest corner of the county. Jewell knew the men and considered them friendly. “You see Wickersham?” he was asked. “Wickersham” was Jesse C. Wickersham, who had a place with his wife about two miles away. Jewell replied he had not seen his neighbor recently. They asked again, “Where Wickersham?” and then, “You come Wickersham?” He promised to ride over the next day and check on his friends. 2
With the weather clear mid-morning on Thursday, Jewell went over but did not approach the cabin, apparently because he saw no smoke from the chimney nor other sign of life. “I had already made up my mind something was wrong,” he told a reporter a few days later, “possibly a murder.” He detoured back to the Indian’s camp about a half-mile away from the Wickersham place, where they had been hired to cut wood. 3
When had anyone last seen a person at the cabin? He asked. Not since mid-morning on Monday; on Wednesday, “they said they had gone down to the house, and fearful of approaching it, they had stood afar off and hallooed for Wickersham, but without an answer.” 4
“Taking the two Indians with me, I attempted to open the door of the sitting-room but found it locked. The window was down and I pulled out the sash. The Indians then suggested that I should come round to the dining-room. I did so. The door did not yield. I went to the window, pulled aside the blind, and there my eyes fell upon the rigid form of my old friend – a blanket about his head and his feet in a pool of blood.” 5
Without investigating further, Jewell immediately returned to his horse and went home, where he fetched his wife and headed towards Skaggs’ Springs, the nearest place where he could seek help. 6
It was fourteen miles to the Skaggs’ Hot Springs resort, where hopefully the telephone and telegraph lines were still up despite the overnight storm winds. Jewell knew the winding road well and in good weather he probably could get there in under three hours. That day it apparently took him twice that long. The weather had made the route treacherous; the next morning the county coroner’s horse would slip and fall along this road enroute to the crime scene.
The long ride probably gave Jewell and his wife time to reflect. They had last seen the Wickershams about three weeks earlier, when the two couples spent the weekend together to celebrate the new year. “We were continually over at each other’s places,” he later told a reporter. But aside from the companionship of being the only neighbors within walking distance, they didn’t have much in common. 7
Jewell was more of a gentleman farmer and the place he called “Castle Rock Ranch” was the couple’s country home. At the time Jewell was 35 and owned the Petaluma News Depot, one of the most important businesses in south county because it handled all newspaper, magazine and book sales. Although his parents were rich he seemingly did well on his own, later owning a hop ranch near Fulton and trying his luck at gold mining in the Yukon. The couple mainly lived in Petaluma before moving on to Santa Cruz and San Francisco.
Jesse C. Wickersham had a very different lifestory. His uncle was Isaac G. Wickersham, the wealthiest man in Sonoma county and president of the National Gold Bank of Petaluma – one of nine banks in the state allowed to actually print money. Jesse was 52 and had lived in his uncle’s shadow for years, working as an assistant cashier and notary at the bank, then as an insurance agent for another of his uncle’s companies. He married the sister of his uncle’s wife, a widow who was his same age. He was also dependent upon his in-laws; he and wife Sarah lived with them in Petaluma, and his father-in-law was co-owner of the ranch.
There was something the matter with Jesse which was never explained. “About Wickersham being poorly – that is true,” said a Healdsburg man who owned property near the ranch. “He is a weakly man – unable to ride and unable to look after the rancho properly.” Jewell agreed he was “in a very sickly condition” when he first moved to the country, but said he was better now and “could ride about and do light work.” 8
Or maybe the problem was psychological. Unlike the Jewells who came and went between their ranch and Petaluma, Jesse and his wife apparently remained there all the time. That they chose to live a reclusive life at one of the most remote places in Sonoma county is worth noting along with his earlier “failure to launch” – never advancing beyond menial clerical jobs, despite the remarkable advantage of his family connections.
Another important detail in his bio: Jesse was a Civil War vet who served almost the entire duration of the war, advancing to First Lieutenant (not Captain, as claimed in some of the contemporary articles). He was in the 2nd Iowa Infantry – where nearly half the regiment was wounded or killed – and fought in some of the worst battles, including Vicksburg, Shiloh and Atlanta; perhaps he had shrapnel that later dangerously shifted in his body, or maybe he had severe PTSD.
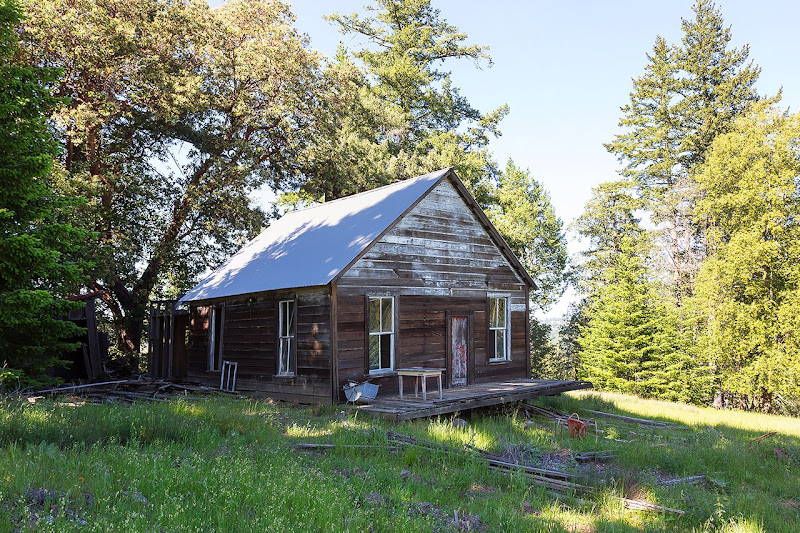 |
| The cabin of Sarah and Jesse Wickersham as seen today. All photos here courtesy David Otero and Wickersham Ranch |
The Jewells reached Skaggs’ Springs in late afternoon and fortunately, both telephone and telegraph lines were functioning – no sure thing in rural Sonoma county even 25 years later, as outlying customers provided the wires to connect to the nearest company office, which in this case was Geyserville.
Jewell either spoke or telegraphed the coroner, sheriff and I. G. Wickersham. Some of the misinformation that spread over the following days was probably due to the lo-fi quality of the telephone connection – the wood cutters were first identified as Italians and not Indians, for example. And soon after that all lines to Skaggs’ Springs went down, blocking reporters from asking questions or receiving any updates for two long days.
Although there was little more than an hour before the last “up-train” departed from Petaluma, the county coroner and marshal were onboard headed north, along with Fred Wickersham, the adult cousin of Jesse. They were joined by others in towns along the way; the party that finally arrived at the Wickersham ranch included at least 17 men and likely more.
It took them around twelve hours to get to the ranch overnight from Cloverdale. The Dry Creek crossing was flooded out; there Sheriff Bishop turned back while the others swam their horses across. Other streams and creeks were swollen from the week’s storms and they also had to swim the horses across Hot Spring creek. The coroner’s horse fell, injuring him and Dr. Swisher “lost his horses” (no further details of what that meant). Healdsburg Constable Truitt called it “one of the hardest trips of my experience.” 9
While they were still slogging through the mud heading to the crime scene, the rest of the county was afire with rumor and gossip. “The news was carried from mouth to mouth, and soon the horror was the theme of conversation on every hand.” 10
The first published article appeared the same evening as Jewell’s telephone calls, which is to say the only known facts were that Wickersham was dead and the whereabouts of his wife and Chinese cook were unknown. The Oakland Tribune set a low bar with its story datelined Santa Rosa: “…there are not a few people here who express the opinion that [Mrs. Wickersham] may have met a fate worse than death to a woman of her character, and that her former servant, after murdering his master may have carried her off to some hiding place, possibly aided by confederate of his own race, for the basest purposes…” 11
Wickersham’s mysterious illness was the core of a widespread rumor the next day. An unnamed man “from near that locality” rode into Santa Rosa and claimed he knew what happened: “…Wickersham, who had been for a long time in low health, died suddenly, while sitting in his chair, from hemorrhage of the lungs. His wife, who had previously dispatched the Chinaman for the doctor, after finding that her husband was dead, threw a blanket over him, and started for the neighbors, fainting on the way.” 12
The hemorrhage theory was chewed over for two days, then forgotten once the bodies were found. But another rumor persisted for weeks – that the Chinese killer had “outraged” Sarah Wickersham. The inquest report did not mention sexual assault and the family vehemently denied it was true. “The statements that have been made in the papers concerning foul outrages are not true, nor are they kind,” Fred Wickersham said the day of the funerals. His banker father also asked for understanding: “Our feelings can better be imagined than described, but it makes the pangs of regret the keener when such reports are spread. It is bad enough, God knows, without making the facts worse.” Ignoring their pleas, newspapers – particularly papers in Sonoma county outside of Petaluma, including Santa Rosa’s Sonoma Democrat – continued to claim she had been raped. 13
Meanwhile, back on the ranch (oh, how I have longed for a chance to use that phrase) the party arrived a few hours after dawn Friday, having ridden all night except for a short rest at Skaggs’ Springs. While others were unsaddling, Constable Truitt was the first to enter the house. This was unfortunate because he was an unreliable figure; he exaggerated his role in the events and gave the press an interpretation of Sarah’s death which contradicted the coroner’s report (he also pushed the “outraged” claim). That he was alone in the house for several minutes casts doubt on whether the crime scene was really undisturbed. 14
When the group entered the cabin they found Truitt examining Jesse’s body, which was in a chair with its back to the fireplace. He had been shot in the back of the head as the couple was sharing a meal.
“He was sitting at the table as though he had fallen asleep,” Marshal Blume told a Santa Rosa reporter. “His head had dropped over to tbe left side slightly and the chin was resting on his breast…The plate was upset in his lap. The plate of his wife, which was opposite, had potatoes on it and was undisturbed. There was a piece of pie at each place. The chair which had been occupied by Mrs. Wickersham was overturned.” 15
There was at least one reporter there who wrote a remarkably detailed account of the scene for the Petaluma Courier. Evidence showed the shotgun blast came from the kitchen doorway:
| The kitchen door on both sides was painted white. On the kitchen side, about four feet from the floor, were marks of powder burn almost as large as a man’s hand. The gun from which the shot was fired that ended the life of the owner of the house was evidently held close against the door, and in that position the muzzle would have been only about five feet from the body of the unsuspecting victim. All present came to the conclusion that the murderer had certainly opened the door only a few inches, thus being able to level his gun on the husband without allowing it to project beyond the edge, while the door screened him from the wife’s view. 16 |
Jesse had another shotgun wound on his right side. The coroner did not say which shot he believed was first, but either of them would have been fatal. The significance of this shot is discussed in part two.
For reasons unknown, someone had tried hard to stop the bleeding before he died. Again from the Courier:
| Beneath the chair on which the body rested were two pools of blood, the clothing worn by the deceased also being saturated. About the neck was twisted a large linen tablecloth, and underneath it several napkins. These were almost as thoroughly soaked with blood as if they had been dipped into a bucket filled with it. From the corners and here and there on the edge only could it be told what the original color of the articles were. From the snowy whiteness of these spots, still stiff with starch, it was evident that the tablecloth was taken from the drawer in which the linen was kept for the express purpose of absorbing the blood. 17 |
Sarah was found in their bedroom. Her wrists were tied behind her back with the same clothesline rope looped around her chest, the end tied to the bed (I’m guessing the rails of a brass bed). She was half-kneeling beside it with her head resting on the bed. She had one shotgun wound to her right side. The bed was neatly made and unruffled. The coroner made no mention of sexual assault, but he also did not describe the condition of her face, which several newspapers described as being “mutilated.” One account claimed her nose was broken and the reliable Petaluma Courier reporter wrote her “face was swollen and bruised.”
And then there was the cake story. “One of the most curious things discovered was a piece of cake, which had been placed by the murderer after accomplishing his diabolical designs on the pillow beside the dead woman. It is said that this is a custom of the Chinese to exorcise evil spirits from the bodies of the dead,” wrote one Healdsburg paper. In another account there were five pieces of cake. 18
There is indeed a religious belief that the spirit of someone who has died violently can become a “hungry ghost,” but it’s hardly a secret that Chinese generally made food offerings to the dead. The meticulous Courier reporter does not mention anything about a piece of cake on the bed; the newspapers that did so were quoting or paraphrasing Marshal Blume or Constable Truitt, who both kept pushing the “outraged” claim even after the Wickersham family asked everyone to knock it off. In short, I don’t think there’s much question that this part of the story was planted in order to prove the Chinese cook had to be the killer.
The cook’s room was also inspected, and will be discussed in part two; all that’s crucial to know is that nothing incriminating was found there except for some clothesline like the rope used to tie up Sarah. Elsewhere in the house someone found Jesse’s meticulously-kept journal with the last entry made after Sunday night supper. That and a burned-dry lamp on the table led them to conclude the murders happened between 5-6PM on Monday, four days earlier.
The house was not ransacked and Wickersham still had his watch and pocket change. “This shows that the object of the fiendish criminal was not robbery,” wrote the San Francisco Chronicle, one of the papers pushing the outraged/cake angle. 19
But at least some times of the year, Jesse kept large amounts of cash around to pay ranch hands. Again the Petaluma Courier seemed to have the last word: “A small satchel, however, in which the rancher was known to sometimes keep money, was found open… No one present was able to state whether there was much or little money in the house before the deed was committed.” The Courier also had an anecdote about Jesse unexpectedly settling a $100 debt with a neighbor – the equivalent of over $3,300 today. Another time he had to defer paying the neighbor because “He had nothing less than a twenty.”
While the Healdsburg doctor did the autopsies, Marshal Blume took a party of the men to search the range for any signs of the cook. Finding nothing, the coroner’s jury heard evidence from the doctor and Elliott Jewell, coming to the conclusion that the Wickershams “came to their death from gunshot wounds, inflicted by unknown hands, ail evidence pointing towards a Chinese cook in the employ of deceased.”
And that was all, except for getting the bodies back to Petaluma for a funeral. It took them until Sunday to reach Healdsburg; the Alta California speculated the bodies were lashed in a wagon which was floated across the flooded creeks. 20
A Santa Rosa paper reported, “In consequence of tbe bad weather and swollen streams great difficulty was experienced in bringing them in. People gathered at every settlement along the roadside to get a sight of the sad procession.” When the bodies finally arrived in Petaluma on the night train, “The crowd that awaited the arrival of the bodies at that depot on Sunday night was a large one, and when the rude coffins were placed upon two express wagons, the citizens forming about escorted the remains to the undertakers.” 21
The funerals were held in Petaluma on Monday, and the San Francisco Chronicle reported on the mood of the town:
| There was a Sunday stillness in the town of Petaluma yesterday. The stores, saloons, and even banks were closed. Conversation was carried on in undertones, but underneath that sorrow lurked a revengeful spirit, which displayed itself by frequent gesture and ill-guarded remark against the race from whom came the murderer that laid low in a foul and bloody death their esteemed town people. There were no Chinese to be seen on the streets. 22 |
Sarah and Jesse were buried in the Wickersham family plot at Cypress Hill Cemetery in Petaluma.
1 The Saint Paul Globe, January 24, 1886
2 “I think Indians are friendly” Jewell inquest testimony, page 3
Dialogue from Jewell interview in Petaluma on January 25. San Francisco Chronicle, January 26, 1886
3 Chronicle, ibid
4 ibid
5 ibid
6 Some accounts state he rode immediately to Skaggs’ Springs, but I found it doubtful that he would leave his wife alone, given that the murderer could still be in the area. Two people traveling in a buggy would also be slower and help explain why the trip took around six hours.
7 Chronicle ibid
8 Interview in Petaluma with J. Seawall on January 22. San Francisco Chronicle, January 23, 1886
op. cit Jewell interview Chronicle, January 26
9 Truitt quoted in the Daily Republican, January 25, 1886
10 Petaluma Argus, January 23, 1886
11 Oakland Tribune, January 22, 1886
12 Sacramento Record-Union, January 23, 1886
13 San Francisco Chronicle, January 26, 1886
14 Truitt interview in the Daily Republican, January 25, 1886
15 Daily Democrat, January 26, 1886
16 Petaluma Courier, January 27, 1886
17 ibid
18 Russian River Flag, January 27 1886
19 San Francisco Chronicle, January 23, 1886
20 Daily Alta California, January 24, 1886
21 Daily Democrat, January 26, 1886
San Francisco Chronicle, January 26, 1886
22 Chronicle, ibid





















